These assets are significant for any business entity because they’re necessary for running operations. Besides, there is a heavy investment involved to acquire the plant assets for any business entity. The company’s top management regularly monitors the plant assets to assess any deviations, discrepancies, or control requirements to avoid misuse of the plant assets and increase the utility.
If debt has been used to purchase the plant asset, then the cash flow statement would also show the regular payments towards that debt too. Plant assets are fixed, long-term assets that are illiquid which means they are difficult to turn to cash. Most other assets are either non-tangible or assets that can be liquidated quickly.
Plant assets, also known as fixed assets, are tangible assets that are used in the production process or to generate revenue for a company over a prolonged period of time. These assets are expected to provide economic benefits to the company beyond the current accounting period. Plant assets are considered non-current assets and are categorized as long-term assets on a company’s balance sheet.
Plant assets are subject to depreciation, which is the process of allocating the cost of an asset over its useful life. Depreciation helps to reflect the gradual loss of value and obsolescence of these assets as they are used in the production process or over time. The rise of mass transportation has increased the focus for businesses to invest in their vehicle fleets. Transportation is one of the most valuable plant assets, but also one of the most expensive the maintain. Like any category of assets, it’s critical to evaluate plant assets on a company-by-company basis.


Plant assets can be any asset used to make money that has both a useful life of more than a year and does not directly become part of the product itself. This makes them different from other types of https://www.bookstime.com/ assets such as liquid assets, inventory, or intellectual assets. The other non-fixed assets can be sold or consumed relatively quickly because they are used for short term projects in a business.
One distinguishing feature of plant assets is that they are not meant for resale. Unlike inventory or stock in trade, plant assets are acquired with the intention of using them in the production process or to support the company’s operations. These assets are expected to have a useful life that extends beyond the current accounting period. Plant assets, also known as fixed assets, are tangible assets that are used in the production process or to generate revenue for a company over an extended period of time. These assets are not meant for resale and are expected to provide economic benefits for several years. From an accounting perspective, plant assets are typically held on the balance sheet at historical cost (what the company paid for them) less depreciation (ongoing wear-and-tear expense) over time.
Depreciation and amortization, or the process of expensing an item over a longer period of time than when it was acquired, are calculated on a straight-line basis. It’s determined by multiplying the difference between an asset’s purchase price and its projected salvage value by the number of years it’ll be in use. Depending on the industry and purpose of a company, a number of items might now qualify as plant assets.
Any asset that will provide an economic benefit within one year is a current asset. Plants are considered a “current asset” because PP&E has a useful life longer than one year. A plant is a physical object that can be used to produce plant assets are defined as a product or service. The second method of deprecation is the declining balance method or written down value method. Every year, the percentage is applied to the remaining value of the asset to find depreciation expense.
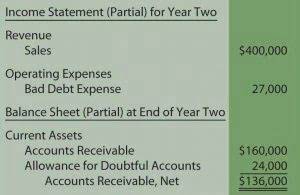
Plant assets, also known as property, plant, and equipment (PP&E), are tangible assets with a useful life of more than one year. The expected useful life of the machine is 7 years, and the salvage (scrap) value after 7 years will be $50,000. Therefore, the first few years of the assets are charged to higher depreciation expenses. The later years are charged a lower sum of depreciation based on the assumption that lower revenue is generated. The straight-line method is the most commonly used method in most business entities. It is also called a fixed-installment method, as equal amounts of depreciation are charged every year over the useful life of an asset.
Оставить комментарий